Topic(s)
Security
Author(s)
Organizations face a myriad of security challenges. From safeguarding industrial control systems to managing third-party risks and navigating the complexities of ransomware attacks, the need for robust security measures has never been more critical. Today we delve into three key areas highlighted in Cyberedge Group’s 2024 Cyberthreat Defense Report: Operational Technology (OT) security, third-party risk management, and the declining success rate of data recovery post-ransomware payment.
The State of OT Security: A Critical Concern
Operational Technology (OT) security, encompassing Industrial Control Systems (ICS) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of organizational security. According to the report, when asked to rate their organization’s overall security posture, respondents placed OT security dead last. This alarming trend underscores the urgent need for organizations to prioritize the protection of their critical infrastructure.
OT systems are integral to the functioning of essential services such as energy, water, and manufacturing. A breach in these systems can have catastrophic consequences, not only for the organization but also for public safety and national security. Despite the high stakes, many organizations continue to underinvest in OT security, leaving their critical infrastructure vulnerable to cyberattacks.
To address this gap, organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to OT security. This includes implementing robust security measures such as network segmentation, continuous monitoring, and incident response planning. Additionally, fostering a culture of security awareness among employees and stakeholders is crucial to ensuring the resilience of OT systems.
Third-Party Risk Management: A Shining Example of GRC Excellence
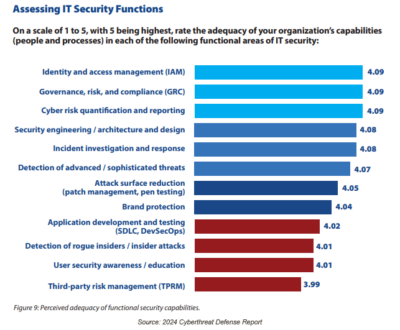
The report also highlights a significant concern in third-party risk management, with respondents rating the adequacy of their organization’s capabilities in this area at the bottom of the list. This finding is particularly concerning given the increasing reliance on third-party vendors and partners in today’s interconnected business environment.
Third-party risk management is a critical component of a comprehensive Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) strategy. It involves assessing and mitigating the risks associated with third-party relationships, including data breaches, compliance violations, and operational disruptions. Despite its importance, many organizations struggle to effectively manage third-party risks, often due to a lack of resources, expertise, or visibility into their third-party ecosystem.
Tackling these challenges can be daunting, but we can help. Our GRC practice has demonstrated exceptional proficiency in third-party risk management. By leveraging advanced risk assessment tools, conducting thorough due diligence, and fostering strong relationships with third-party vendors, we have successfully mitigated potential risks and ensured compliance with regulatory requirements.
Organizations looking to enhance their third-party risk management capabilities should include these key strategies:
- Comprehensive Vendor Risk Assessments: Conducting detailed assessments of third-party vendors to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Vendor Monitoring: Implementing ongoing monitoring processes to identify and mitigate potential risks, ensuring ongoing compliance and security.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Building strong, collaborative relationships with third-party vendors to ensure alignment on security and compliance objectives.
- Training and Awareness: Education of your security and compliance teams on the importance of third-party risk management and providing regular updates to keep them informed of best practices and emerging third-party threats.
Ransomware Resilience: The Declining Success of Data Recovery
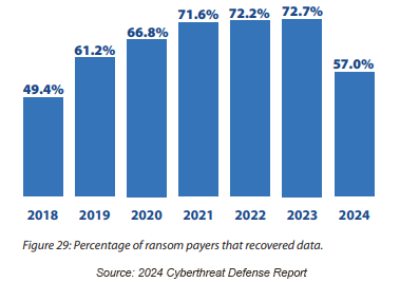
Ransomware attacks continue to pose a significant threat to organizations worldwide. The report notes a troubling trend: the percentage of companies that paid the ransom and were able to recover their data is declining. This decline highlights a critical issue—many criminal organizations lack the technical expertise to ensure that victims who pay the ransom can fully restore their services.
This trend serves as a stark reminder that paying the ransom is not a guaranteed solution to ransomware attacks. In fact, it often exacerbates the problem by encouraging further criminal activity and leaving organizations with incomplete or corrupted data. To effectively combat ransomware, organizations must focus on prevention, preparedness, and resilience.
Key strategies for enhancing ransomware resilience include:
- Regular Backups: Implementing regular, immutable (secure) backups of critical data to ensure that it can be restored without paying a ransom.
- Incident Response Planning: Developing and testing comprehensive incident response plans to ensure a swift and effective response to ransomware attacks.
- Employee Training: Educating employees on how to recognize and respond to phishing attempts and other common ransomware delivery methods.
- Advanced Security Measures: Deploying advanced security technologies such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) and network segmentation to detect and mitigate ransomware threats.
In conclusion, the findings from the recent security report underscore the importance of addressing key areas such as OT security, third-party risk management, and ransomware resilience. By prioritizing these areas and implementing robust security measures, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and better protect themselves against the evolving threat landscape.
Tackling these challenges can be daunting, but we can help. Our GRC practice has demonstrated exceptional proficiency in third-party risk management.

